01-python-pandas-overview
1. Pandas之:Pandas简洁教程
简介
pandas是建立在Python编程语言之上的一种快速,强大,灵活且易于使用的开源数据分析和处理工具,它含有使数据清洗和分析⼯
作变得更快更简单的数据结构和操作⼯具。pandas经常和其它⼯具⼀同使⽤,如数值计算⼯具NumPy和SciPy,分析库statsmodels和scikit-learn,和数据可视化库matplotlib等。
pandas是基于NumPy数组构建的,虽然pandas采⽤了⼤量的NumPy编码⻛格,但⼆者最⼤的不同是pandas是专⻔为处理表格和混杂数据设计的。⽽NumPy更适合处理统⼀的数值数组数据。
本文是关于Pandas的简洁教程。
对象创建
因为Pandas是基于NumPy数组来构建的,所以我们在引用的时候需要同时引用Pandas和NumPy:
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: import pandas as pdPandas中最主要的两个数据结构是Series和DataFrame。
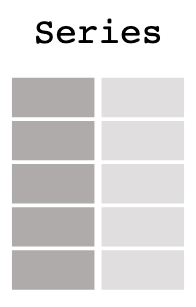
Series和一维数组很相似,它是由NumPy的各种数据类型来组成的,同时还包含了和这组数据相关的index。
我们来看一个Series的例子:
In [3]: pd.Series([1, 3, 5, 6, 8])
Out[3]:
0 1
1 3
2 5
3 6
4 8
dtype: int64左边的是索引,右边的是值。因为我们在创建Series的时候并没有指定index,所以index是从0开始到n-1结束。
Series在创建的时候还可以传入np.nan表示空值:
DataFrame是⼀个表格型的数据结构,它含有⼀组有序的列,每列可以是不同的值类型(数值、字符串、布尔值等)。
DataFrame既有⾏索引也有列索引,它可以被看做由Series组成的字典(共⽤同⼀个索引)。
看一个创建DataFrame的例子:
上面我们创建了一个index的list。
然后使用这个index来创建一个DataFrame:
上面的DataFrame接收三个参数,第一个参数是DataFrame的表格数据,第二个参数是index的值,也可以看做是行名,第三个参数是列名。
还可以直接传入一个字典来创建一个DataFrame:
上面的DataFrame中,每个列都有不同的数据类型。
我们用个图片来更好的理解DataFrame和Series:
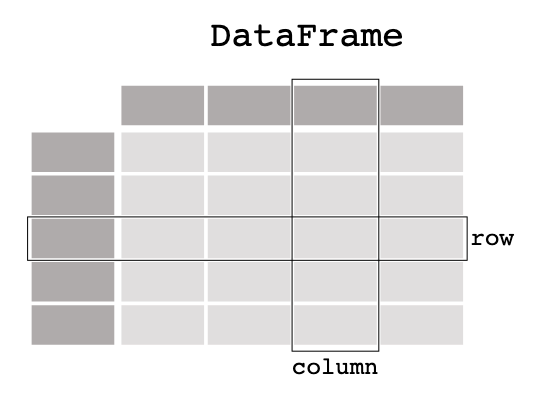
它就像是Excel中的表格,带有行头和列头。
DataFrame中的每一列都可以看做是一个Series:
查看数据
创建好Series和DataFrame之后,我们就可以查看他们的数据了。
Series可以通过index和values来获取其索引和值信息:
DataFrame可以看做是Series的集合,所以DataFrame带有更多的属性:
head跟tail分别取得DataFrame的头几行和尾部几行。
同样的DataFrame也有index和columns:
describe方法可以对数据进行统计:
还可以对DataFrame进行转置:
可以按行和按列进行排序:
选择数据
通过DataFrame的列名,可以选择代表列的Series:
通过切片可以选择行:
或者这样:
loc和iloc
使用loc可以使用轴标签来选取数据。
前面是行的选择,后面是列的选择。
还可以指定index的名字:
如果index的名字不是切片的话,将会给数据降维:
如果后面列是一个常量的话,直接返回对应的值:
iloc是根据值来选取数据,比如我们选择第三行:
它其实和df.loc['2020-12-04']是等价的:
同样可以传入切片:
可以传入list:
取具体某个格子的值:
布尔索引
DataFrame还可以通过布尔值来进行索引,下面是找出列A中所有元素大于0的:
或者找出整个DF中,值大于0的:
可以给DF添加一列:
使用isin()来进行范围值的判断判断:
处理缺失数据
现在我们的df有a,b,c,d,e这5列,如果我们再给他加一列f,那么f的初始值将会是NaN:
我们给前面的两个F赋值:
可以drop所有为NaN的行:
可以填充NaN的值:
可以对值进行判断:
合并
DF可以使用Concat来合并多个df,我们先创建一个df:
然后把DF拆成三部分:
最后把使用concat把他们合起来:
还可以使用join来进行类似SQL的合并:
分组
先看上面的DF:
我们可以根据key来进行group,从而进行sum:
group还可以按多个列进行:
本文已收录于 www.flydean.com
最通俗的解读,最深刻的干货,最简洁的教程,众多你不知道的小技巧等你来发现!
欢迎关注我的公众号:「程序那些事」,懂技术,更懂你!
最后更新于
这有帮助吗?